Administrer son serveur en web avec cockpit (Debian)
Table des matières
Cockpit est une interface web permettant d'administrer son système.
Il fonctionne sous Debian mais aussi d'autres systèmes
Il existe de nombreux modules, permettant de garnir le panneau d'administration Cockpit.
Nous allons voir comment l'installer sous Debian.
On installe le logiciel cockpit :
On active au démarrage cockpit et on le démarre :
Ensuite, on accède à Cockpit sur l'adresse IP du serveur, port 9090 :
https://serveurdebian:9090
On se connectera avec un compte administrateur.
On pourra installer des paquets supplémentaires pour permettre les fonctions suivantes : (j'ai laissé les descriptions en Anglais, du gestionnaire de paquets) :
cockpit-389-ds : Cockpit UI Plugin for configuring and administering the 389 Directory Server
cockpit-bridge : Cockpit bridge server-side component
cockpit-dashboard : Cockpit remote servers and dashboard
cockpit-docker : Cockpit user interface for Docker containers
cockpit-doc : Cockpit deployment and developer guide
cockpit-machines : Cockpit user interface for virtual machines
cockpit-networkmanager : Cockpit user interface for networking, using NetworkManager
cockpit-packagekit : Cockpit user interface for packages
cockpit-pcp : Cockpit PCP integration
cockpit-storaged : Cockpit user interface for storage, using udisks
cockpit-system : Cockpit admin interface package for configuring and troubleshooting a system
cockpit-ws : Cockpit Web Service
Celles que j'installe toujours sont :

Introduction
Cockpit est une interface web permettant d'administrer son système.
Il fonctionne sous Debian mais aussi d'autres systèmes
Il existe de nombreux modules, permettant de garnir le panneau d'administration Cockpit.
Nous allons voir comment l'installer sous Debian.
Installer Cockpit
On installe le logiciel cockpit :
Code BASH :
apt install cockpitOn active au démarrage cockpit et on le démarre :
Code BASH :
systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
Ensuite, on accède à Cockpit sur l'adresse IP du serveur, port 9090 :
https://serveurdebian:9090
On se connectera avec un compte administrateur.
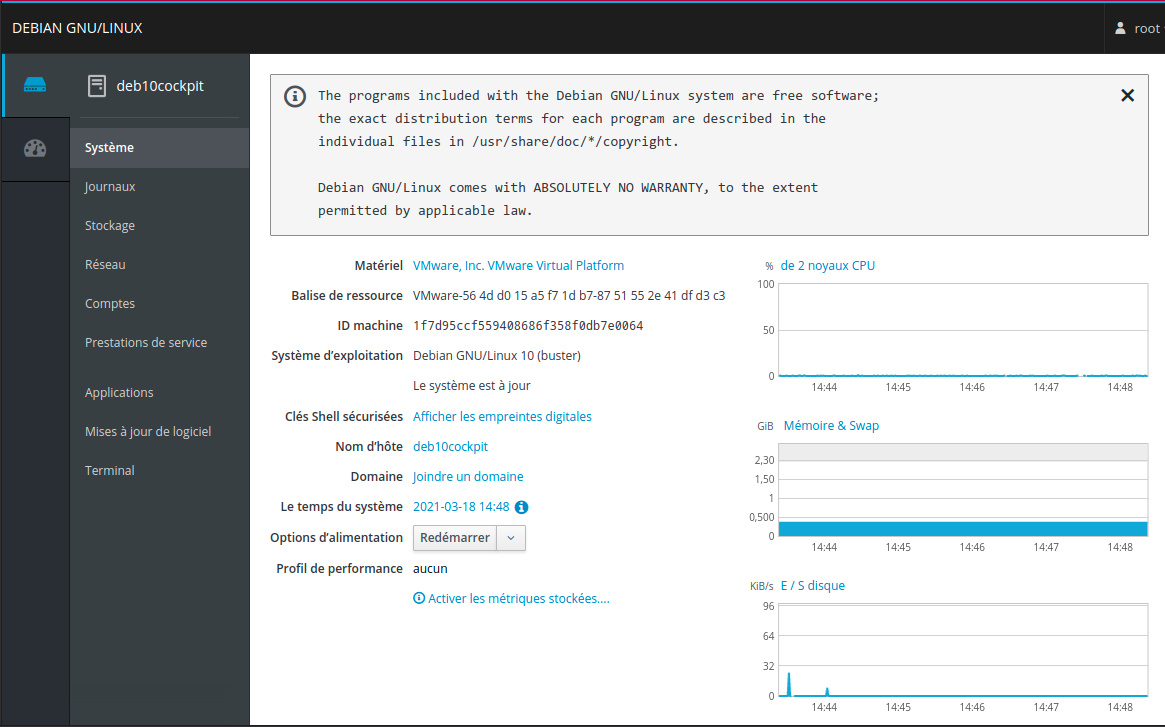
Enrichir Cockpit avec des modules
On pourra installer des paquets supplémentaires pour permettre les fonctions suivantes : (j'ai laissé les descriptions en Anglais, du gestionnaire de paquets) :
cockpit-389-ds : Cockpit UI Plugin for configuring and administering the 389 Directory Server
cockpit-bridge : Cockpit bridge server-side component
cockpit-dashboard : Cockpit remote servers and dashboard
cockpit-docker : Cockpit user interface for Docker containers
cockpit-doc : Cockpit deployment and developer guide
cockpit-machines : Cockpit user interface for virtual machines
cockpit-networkmanager : Cockpit user interface for networking, using NetworkManager
cockpit-packagekit : Cockpit user interface for packages
cockpit-pcp : Cockpit PCP integration
cockpit-storaged : Cockpit user interface for storage, using udisks
cockpit-system : Cockpit admin interface package for configuring and troubleshooting a system
cockpit-ws : Cockpit Web Service
Celles que j'installe toujours sont :
Exemples
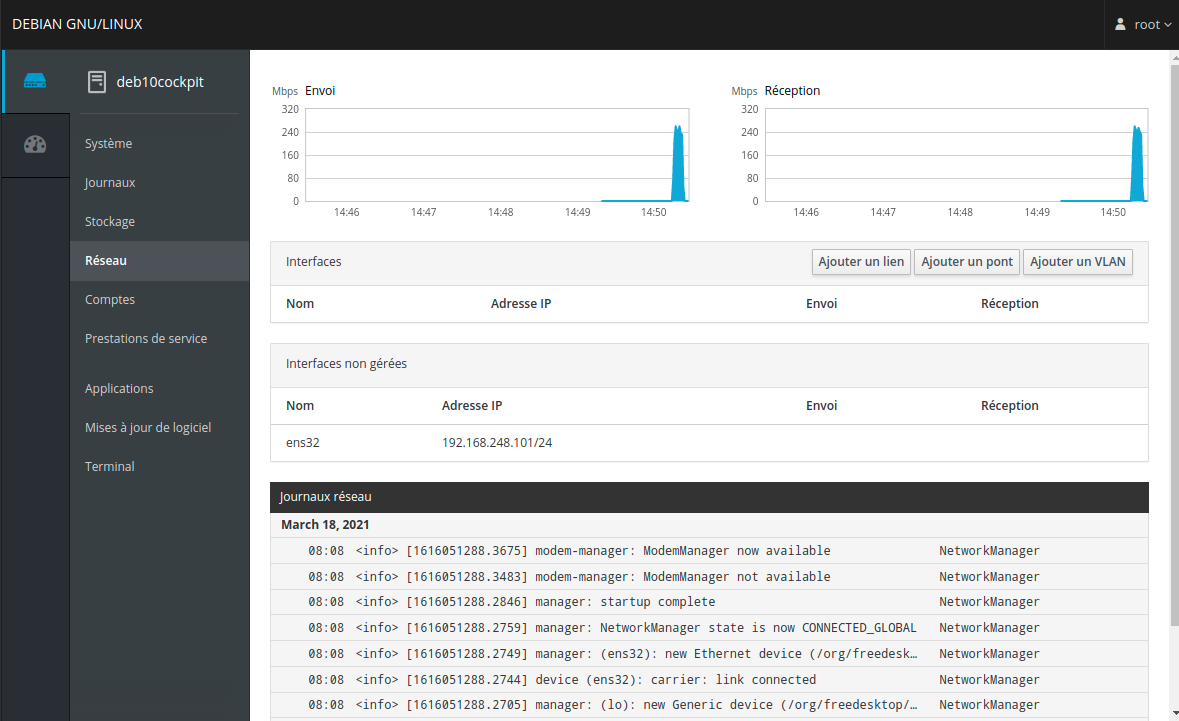
Cockpit module Réseau
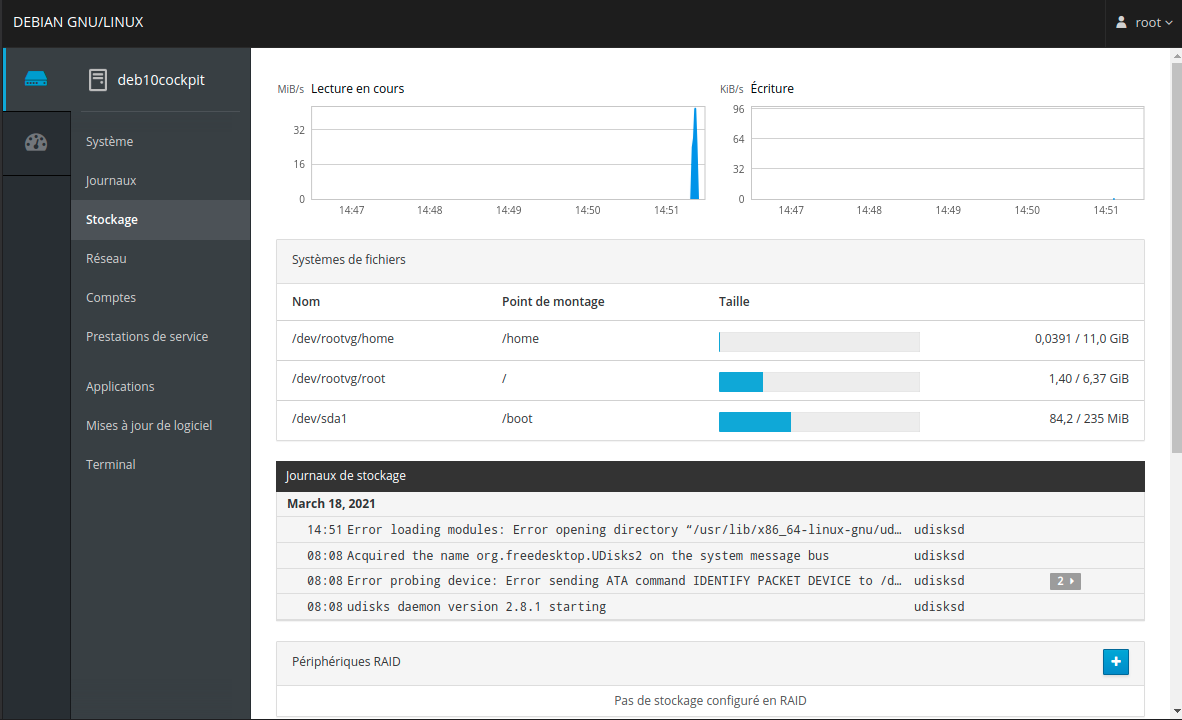
Cockpit module Stockage
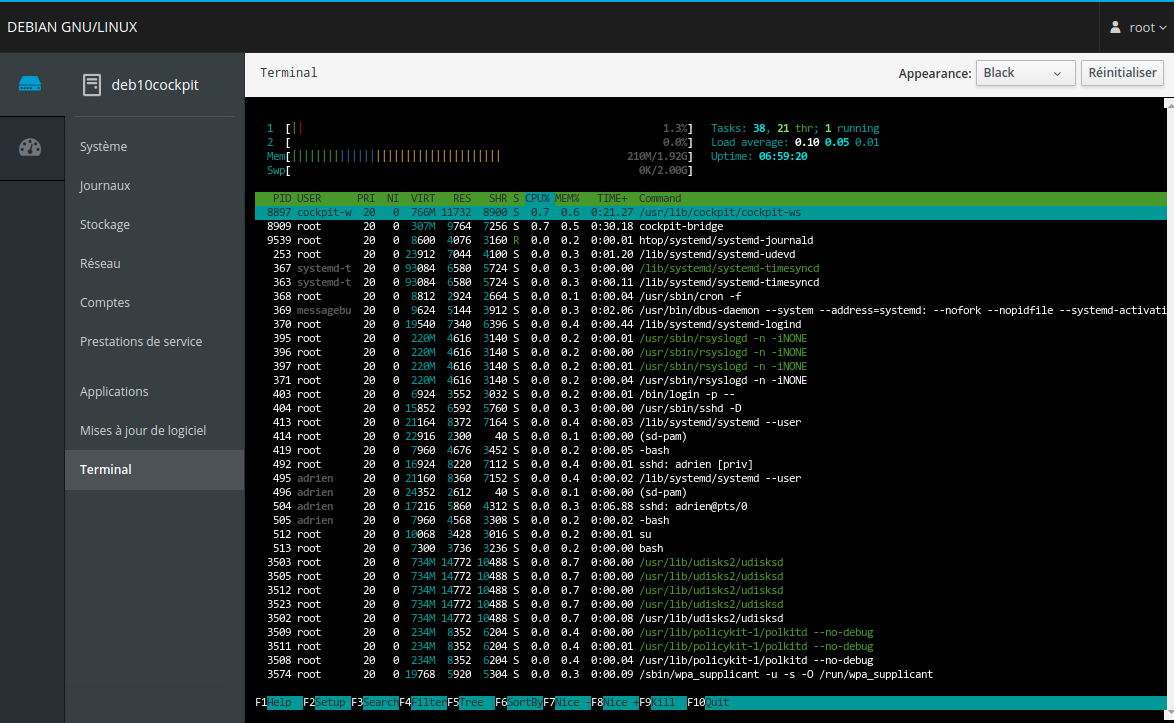
Cockpit module Teminal